Sensing Voltage Dynamics with Differential Intensity Surface Plasmon Resonance Systems
From Applied Optics Wiki
Project Summary
- This project is directed at researching the capacity of surface plasmon resonance systems for label-free detection of the electrical signals that are generated by the excitable cells. Electrical signals are important in communication and control in biological systems. Therefore, accurate and reliable measurements of these signals at the cell level provide valuable in vitro models for physiological and pharmacological investigations. Unlike the popular fluorescent and micro-electrode techniques, surface plasmon resonance is a label-free, non-invasive way to measure localised signals at the cell-sensor interface.
- Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors are conventionally used to detect molecular interactions at the metal-dielectric interface. Additionally, they demonstrated the ability to detect the externally-applied voltage, which characterises them as electrodes with optical readout. As the project is motivated by resolving weak signals associated with dynamic processes, it aims to (i) estimate the limit of voltage detection of SPR using theoretical and experimental approaches and (ii) investigate the response time of the sensors to demonstrate the ability of the technique to resolve the transient electrical signals.
Voltage Sensing System
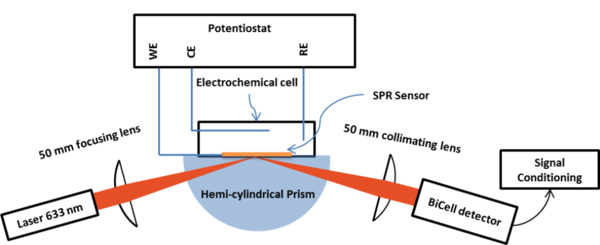
|
- To explore the voltage sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance systems, a voltage sensing system has been designed and tested, which combines SPR optical sensing configuration with an electrochemical unit. The optical configuration is used to excite surface plasmons at the metal-electrolyte interface while the electrochemical unit is used to control the potential at this interface. The applied potential is recorded with the optical system and the electrochemical system simultaneously.
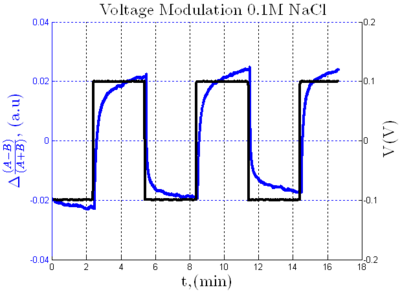
|